Mastering 301 Redirects: A Complete Guide to Protecting Your SEO

Introduction
In the world of digital marketing and SEO, changes to your website are inevitable. Whether you’re updating old content, restructuring your site, or moving to a new domain, these modifications can have significant implications for your site’s search engine rankings. One of the most critical tools you can use to protect your SEO during these transitions is the 301 redirect.
A 301 redirect is more than just a technical fix; it’s a strategic tool that ensures your site maintains its search visibility and authority. This comprehensive guide will take you through everything you need to know about 301 redirects, including what they are, why they’re essential for SEO, how to implement them, and common pitfalls to avoid. We’ll also compare 301 redirects with other types of redirects to help you understand their unique value.
What Is a 301 Redirect?
A 301 redirect is an HTTP status code that signals a permanent move of a webpage from one URL to another. When a 301 redirect is in place, both users and search engines are automatically directed from the old URL to the new one. This seamless transition is crucial for preserving your website’s SEO performance, as it ensures that the authority of the old URL is passed on to the new one.
Key Features of 301 Redirects
- Permanent Move: The 301 status code tells search engines that the old URL has been permanently moved to a new location.
- SEO Preservation: The redirect transfers the SEO value (including PageRank and link equity) of the old URL to the new URL, helping to maintain your site’s rankings.
- User Experience: By automatically redirecting users to the correct page, 301 redirects prevent 404 errors and enhance the overall user experience.
Why Are 301 Redirects Crucial for SEO?
The primary reason 301 redirects are so important for SEO is that they allow you to preserve the authority and rankings of your site even when URLs change. Without a proper 301 redirect, the old URL could lose its ranking in search engine results pages (SERPs), leading to a significant drop in traffic and potentially damaging your site’s overall SEO performance.
SEO Benefits of 301 Redirects

- Maintains Search Rankings: A 301 redirect ensures that the SEO value of the old URL is passed on to the new one, helping to maintain your site’s position in SERPs.
- Prevents 404 Errors: By redirecting old URLs to new ones, you can avoid 404 errors that frustrate users and can lead to increased bounce rates.
- Facilitates Smooth Migrations: Whether you’re restructuring your website, merging content, or moving to a new domain, 301 redirects help ensure that your site’s authority and traffic are preserved during the transition.
When to Use 301 Redirects
301 redirects are essential in a variety of scenarios. Understanding when to use them can help you protect your SEO efforts and ensure a seamless user experience.
Common Scenarios for Using 301 Redirects
- URL Changes: If you update the URL of a page to improve SEO, such as adding keywords, you’ll need a 301 redirect to ensure that the old URL’s authority is passed on to the new one.
- Content Consolidation: When merging multiple pages into a single, more comprehensive page, 301 redirects ensure that the SEO value of the old pages is transferred to the new one.
- Domain Migration: If you’re moving your website to a new domain, 301 redirects are crucial for transferring the SEO authority from the old domain to the new one.
- Deleting Outdated Content: When removing outdated or low-performing content, redirecting the old URLs to relevant pages prevents 404 errors and preserves link equity.
How to Implement 301 Redirects
Implementing 301 redirects may seem daunting, but it’s a straightforward process once you understand the basics. The method you use will depend on your website’s platform and server configuration.
Implementing 301 Redirects on Popular Platforms
1. WordPress
For WordPress users, the process is simplified by plugins like Yoast SEO or Redirection. These plugins allow you to manage 301 redirects directly from the WordPress dashboard without needing to write code.
Example using Redirection plugin:
- Navigate to Tools > Redirection.
- Enter the old URL in the Source URL field.
- Enter the new URL in the Target URL field.
- Click Add Redirect to save the changes.
2. Webflow
Webflow users can set up 301 redirects by accessing the “Project Settings” under the “Hosting” tab. Here, you can specify old and new URLs to create a redirect.
- Go to Project Settings > Hosting > 301 Redirects.
- Enter the old path in the Old Path field (e.g., /old-page).
- Enter the new path in the New Path field (e.g., /new-page).
- Click Save to apply the redirect.
3. NGINX and Apache Servers
For websites hosted on NGINX or Apache servers, 301 redirects are implemented by editing the server configuration files.
- NGINX Example: rewrite ^/old-page$ http://www.example.com/new-page permanent;
- Apache Example (.htaccess): Redirect 301 /old-page http://www.example.com/new-page
These methods provide flexibility and control but require a basic understanding of server management.
Best Practices for 301 Redirects
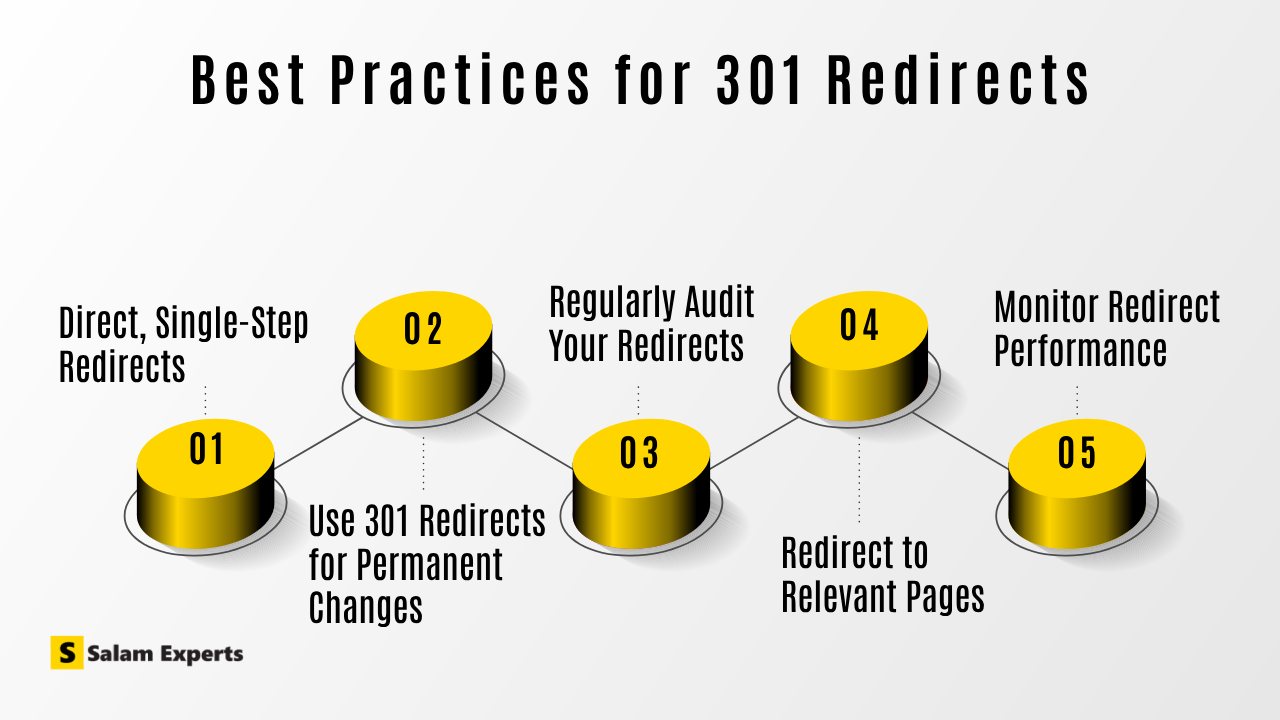
To maximize the SEO benefits of 301 redirects, it’s important to follow best practices to implement them effectively and efficiently.
- Direct, Single-Step Redirects: Avoid creating redirect chains where one URL redirects to another, which then redirects to yet another URL. These chains can slow down your site’s performance and dilute the SEO value passed on to the final URL. Always redirect directly from the old URL to the final destination.
- Use 301 Redirects for Permanent Changes: Ensure you’re using 301 redirects only for permanent changes. If the move is temporary, a 302 redirect is more appropriate, as it tells search engines that the change is not permanent, preserving the original URL’s authority.
- Regularly Audit Your Redirects: Over time, as your website evolves, some redirects may become outdated or unnecessary. Regularly audit your redirects to ensure they’re still relevant and effective. Remove any redundant redirects to improve site performance.
- Redirect to Relevant Pages: Whenever possible, redirect old URLs to pages that are closely related in content. This helps preserve user experience and ensures that the SEO value is passed on in a contextually relevant way.
- Monitor Redirect Performance: After implementing 301 redirects, it’s important to monitor their performance using tools like Google Search Console or Google Analytics. This will help you identify any issues, such as increased 404 errors or drop-offs in traffic, allowing you to make necessary adjustments.
Common 301 Redirect Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Even with the best intentions, it’s easy to make mistakes when implementing 301 redirects. Being aware of common pitfalls can help you avoid costly SEO errors.
- Redirect Chains: A redirect chain occurs when a URL redirects to another URL, which then redirects to yet another URL. These chains can slow down your site’s loading time and dilute the SEO value passed on to the final URL. Always aim for a direct, single-step redirect from the old URL to the final destination.
- Redirect Loops: A redirect loop happens when a URL redirects back to itself, causing an infinite loop that can crash browsers and prevent users from accessing your site. Always double-check your redirects to ensure that no loops are created.
- Using 302 Redirects Instead of 301s: 302 Redirects are meant for temporary changes, and using them for permanent moves can prevent search engines from passing on the SEO value to the new URL. Make sure to use a 301 redirect when the change is permanent.
- Failing to Implement Redirects: When URLs change or content is deleted, failing to implement a 301 redirect can result in 404 errors. These errors not only harm user experience but can also lead to lost rankings and traffic. Always ensure that a 301 redirect is in place whenever a URL changes.
301 Redirects vs. Other Types of Redirects
While 301 redirects are the most common type of redirect used in SEO, it’s important to understand how they differ from other types of redirects.
301 Redirect
- Permanent Move: Indicates that the content has permanently moved to a new URL.
- SEO Value Transfer: Passes almost all of the original URL’s SEO value to the new URL.
302 Redirect
- Temporary Move: Indicates that the content is temporarily located at a different URL.
- No SEO Value Transfer: Retains the original URL’s SEO value, which can cause issues if left in place for too long.
307 Redirect
Temporary Redirect (HTTP 1.1): Similar to a 302 redirect, but used in HTTP 1.1 environments. It indicates that the resource has been temporarily moved to a new URL and should be requested at the original URL in future requests.
Meta Refresh: Meta Refresh
Client-Side Redirect: A type of redirect that occurs on the client side rather than the server side. It is often slower and can negatively impact SEO, as search engines may not transfer the full SEO value to the new URL.
Conclusion
301 redirects are a fundamental component of technical SEO, playing a crucial role in maintaining your website’s search rankings and user experience during periods of change.