How to Resolve Excluded by Noindex Tag Issue in GSC

Managing your website’s visibility on Google is crucial, especially when you notice pages being excluded by the ‘noindex’ tag in Google Search Console (GSC). Whether you’re a seasoned SEO expert or just beginning to manage your own site, understanding and resolving this issue is key to ensuring that your important pages get properly indexed. This guide will help you navigate the problem, explaining what the ‘noindex’ tag is, why it might be applied, and how to address it effectively.
Table of Contents
ToggleIdentifying and Fixing URLs That Should Be Indexed
Sometimes, Google flags URLs that actually should be indexed. Here’s a step-by-step approach to correct this:
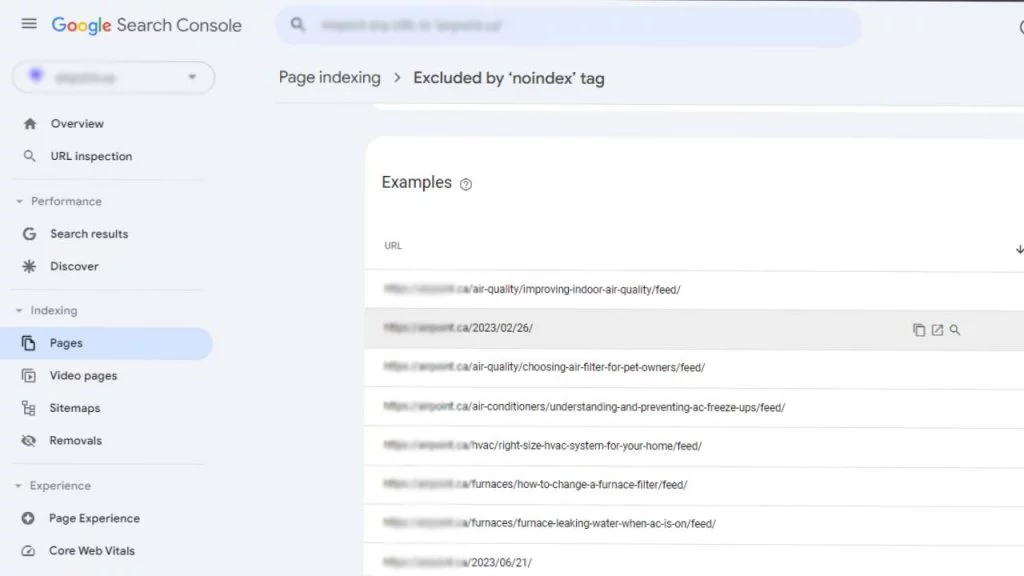
1. Inspect the URL:
- Open Google Search Console.
- Locate the issue in the Page Indexing report.
- Click on the inspection icon next to the affected URL to review its details.
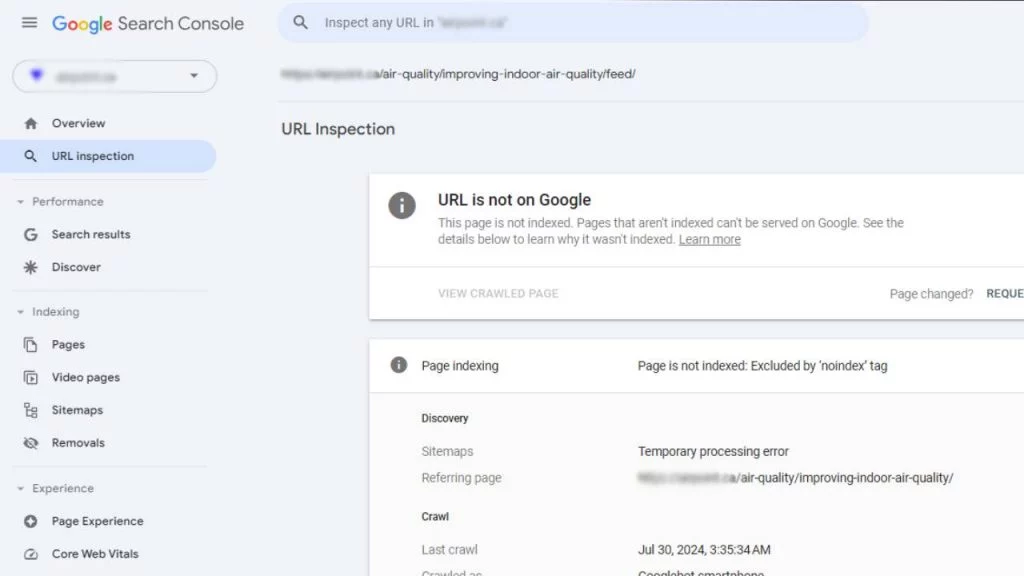
2. Conduct a Live Test:
- After inspecting the URL, select “Test live URL” to assess the current status of the page.
- Check under Availability > Indexing > Indexing allowed? to see if the ‘noindex’ directive is still present.
3. Review the Live Test Result:
- The test results will help you determine if the page is still marked with the ‘noindex’ tag.
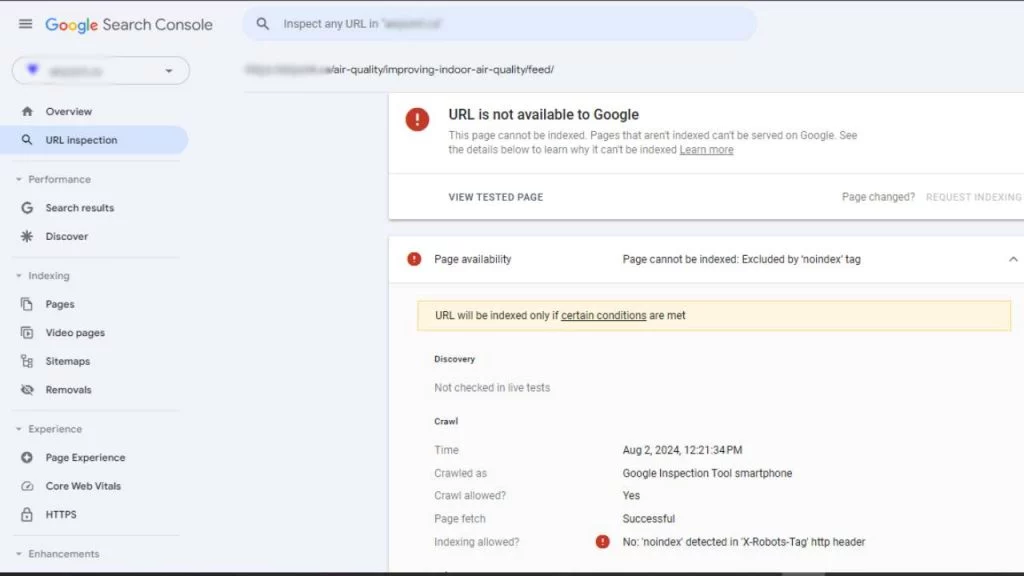
4. Remove the Noindex Tag:
- If the ‘noindex’ directive appears in the page’s robots meta tag, you’ll need to remove it by editing the page’s source code or updating the settings in your CMS.
- If the ‘noindex’ is in the HTTP header, modify the server response to eliminate the directive.
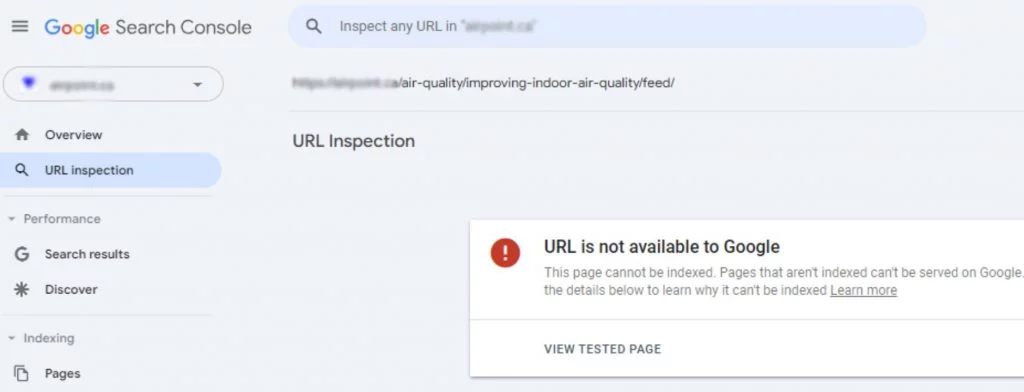
5. Request Indexing:
- If the ‘noindex’ directive is no longer present, or if it was a false positive, request Google to re-crawl the page.
- Click on “Request Indexing” to have Google update its records and remove the URL from the ‘noindex’ list.
When to Ignore Intentionally 'Noindexed' Pages
Not all pages need to be indexed. Here are common examples where a ‘noindex’ directive is applied intentionally:
- Development or Staging Pages: Often used for testing, these pages shouldn’t appear in search results.
- Duplicate Content: To avoid penalties from search engines, pages with duplicate content are marked with ‘noindex’.
- Low-Value Content Pages: Pages like tag archives or thin content pages are often set to ‘noindex’ to enhance the quality of your indexed pages.
Understanding How to Apply a 'Noindex' Directive
1. Using a Noindex Meta Tag:
- A ‘noindex’ meta tag is an HTML tag placed in the source code of a webpage, telling search engines not to index the page. It’s useful for pages like login screens, thank you pages, or admin areas.
<meta name=”robots” content=”noindex”>
2. Utilizing a Noindex HTTP Header:
- Similar to the meta tag, a ‘noindex’ HTTP header is added at the server level. This directive is included in the HTTP response and also instructs search engines not to index the page.
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
X-Robots-Tag: noindex
3. Handling Pages That Shouldn’t Be Indexed
Certain types of pages are better left out of Google’s index to improve your site’s overall performance and visibility:
- Filter URLs
- Search URLs
- Cart, Checkout, and
- Account URLs
Blocking these pages in your robots.txt file can help manage your site’s crawl budget, ensuring that Google focuses on more valuable content. Additionally, URLs used for tracking, such as those generated by pixel managers, typically don’t need to be indexed and can be safely ignored.
Finally
Addressing the ‘Excluded by Noindex Tag’ issue in Google Search Console requires a clear understanding of ‘noindex’ directives and the correct approach to resolving them. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can ensure that your important pages are properly indexed, thereby optimizing your site’s visibility in search results.
FAQs
A ‘noindex’ meta tag is an HTML element that instructs search engines not to index a specific webpage.
URLs are marked ‘noindex’ to prevent certain pages, such as admin pages or duplicate content, from appearing in search results.
You can remove a ‘noindex’ directive by editing the page’s HTML source to delete the meta tag or by modifying the server’s HTTP header response.
No, feed URLs generally don’t need to be indexed, so no action is necessary for these URLs.
You can use Google Search Console’s URL inspection tool or check the page source and response headers for a ‘noindex’ directive.
Author
-

We are a digital marketing agency with over 17 years of experience and a proven track record of helping businesses succeed. Our expertise spans businesses of all sizes, enabling them to grow their online presence and connect with new customers effectively. In addition to offering services like consulting, SEO, social media marketing, web design, and web development, we pride ourselves on conducting thorough research on top companies and various industries. We compile this research into actionable insights and share it with our readers, providing valuable information in one convenient place rather than requiring them to visit multiple websites. As a team of passionate and experienced digital marketers, we are committed to helping businesses thrive and empowering our readers with knowledge and strategies for success.
View all posts





